Bayesian Decision Making for Binary Endpoints
Source:vignettes/binary-endpoints.Rmd
binary-endpoints.Rmd
library(BayesianQDM)
library(dplyr)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
library(tidyr)
library(ggplot2)Introduction
The BayesianQDM package provides comprehensive methods for Bayesian quantitative decision-making in clinical trials with binary endpoints. This vignette demonstrates how to use the package for calculating posterior probabilities, posterior predictive probabilities, and Go/NoGo/Gray decision probabilities.
Basic Concepts
Decision Framework
The Bayesian decision-making framework categorizes trial outcomes into three zones:
- Go: Evidence suggests the treatment is effective (proceed to next phase)
- NoGo: Evidence suggests the treatment is not effective (stop development)
- Gray: Evidence is inconclusive (may need additional data)
Basic Examples
Posterior Probability
# Calculate posterior probability for a controlled design
posterior_prob <- pPPsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior',
design = 'controlled',
theta0 = 0.15,
n1 = 20, n2 = 20, y1 = 12, y2 = 8,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = NULL, ne2 = NULL, ye1 = NULL, ye2 = NULL, ae1 = NULL, ae2 = NULL
)
cat("Posterior probability that treatment effect > 0.15:", round(posterior_prob, 4))
#> Posterior probability that treatment effect > 0.15: 0.3871Posterior Predictive Probability
# Calculate posterior predictive probability
predictive_prob <- pPPsinglebinary(
prob = 'predictive',
design = 'controlled',
theta0 = 0.15,
n1 = 20, n2 = 20, y1 = 12, y2 = 8,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
m1 = 50, m2 = 50,
ne1 = NULL, ne2 = NULL, ye1 = NULL, ye2 = NULL, ae1 = NULL, ae2 = NULL
)
cat("Predictive probability for future trial:", round(predictive_prob, 4))
#> Predictive probability for future trial: 0.4035Go/NoGo/Gray Decision Probabilities
Basic Usage
# Calculate Go/NoGo/Gray probabilities
result <- pGNGsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior',
design = 'controlled',
theta.TV = 0.3, theta.MAV = 0.1, theta.NULL = NULL,
gamma1 = 0.8, gamma2 = 0.2,
pi1 = c(0.3, 0.5, 0.7),
pi2 = rep(0.2, 3),
n1 = 20, n2 = 20,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
z = NULL, m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = NULL, ne2 = NULL, ye1 = NULL, ye2 = NULL, ae1 = NULL, ae2 = NULL
)
print(result)
#> pi1 pi2 Go Gray NoGo
#> 1 0.3 0.2 0.007803538 0.1821623 0.81003417
#> 2 0.5 0.2 0.192004138 0.5121603 0.29583556
#> 3 0.7 0.2 0.716236863 0.2583638 0.02539935Operating Characteristics
Evaluating Across Scenarios
# Evaluate operating characteristics across different response rates
oc_results <- pGNGsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior',
design = 'controlled',
theta.TV = 0.2, theta.MAV = 0.05, theta.NULL = NULL,
gamma1 = 0.8, gamma2 = 0.2,
pi1 = seq(0.2, 0.6, by = 0.1),
pi2 = rep(0.2, 5),
n1 = 25, n2 = 25,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
z = NULL, m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = NULL, ne2 = NULL, ye1 = NULL, ye2 = NULL, ae1 = NULL, ae2 = NULL
)
print(oc_results)
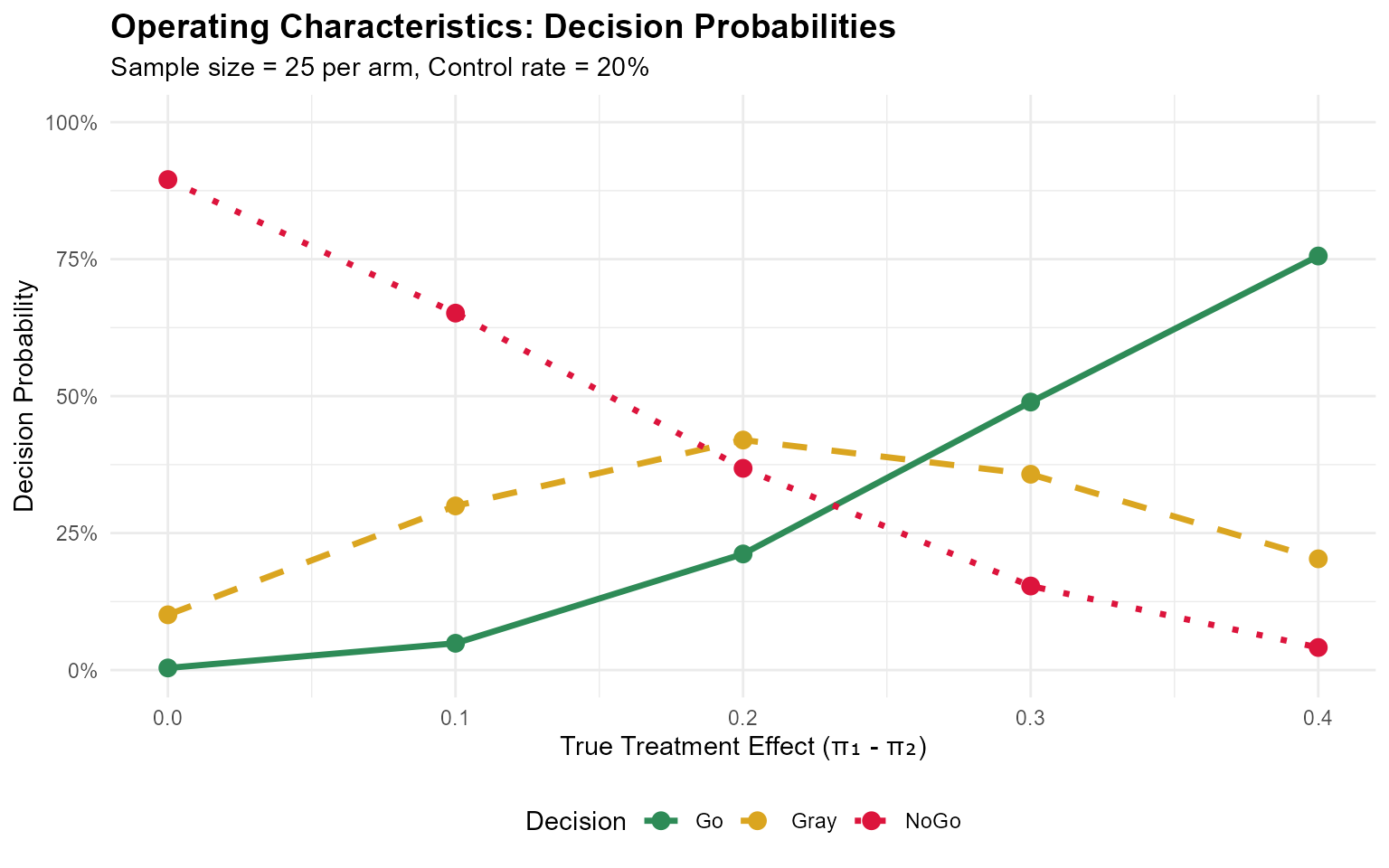
#> pi1 pi2 Go Gray NoGo
#> 1 0.2 0.2 0.003871119 0.1008739 0.89525497
#> 2 0.3 0.2 0.048889816 0.2996013 0.65150893
#> 3 0.4 0.2 0.211943660 0.4198488 0.36820753
#> 4 0.5 0.2 0.489175480 0.3574133 0.15341120
#> 5 0.6 0.2 0.755770714 0.2030452 0.04118413Visualizing Decision Probabilities
# Reshape data for plotting
plot_data <- oc_results %>%
select(pi1, pi2, Go, NoGo, Gray) %>%
pivot_longer(cols = c(Go, NoGo, Gray),
names_to = "Decision",
values_to = "Probability") %>%
mutate(TreatmentEffect = pi1 - pi2)
ggplot(plot_data, aes(x = TreatmentEffect, y = Probability, color = Decision, linetype = Decision)) +
geom_line(linewidth = 1.2) +
geom_point(size = 3) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("Go" = "#2E8B57", "Gray" = "#DAA520", "NoGo" = "#DC143C")) +
scale_linetype_manual(values = c("Go" = "solid", "Gray" = "dashed", "NoGo" = "dotted")) +
labs(
title = "Operating Characteristics: Decision Probabilities",
subtitle = "Sample size = 25 per arm, Control rate = 20%",
x = "True Treatment Effect (π₁ - π₂)",
y = "Decision Probability"
) +
scale_y_continuous(limits = c(0, 1), labels = scales::percent) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
plot.title = element_text(face = "bold", size = 14),
legend.position = "bottom"
)
Study Designs
Controlled Design
Standard two-arm randomized controlled trial.
result_controlled <- pPPsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior',
design = 'controlled',
theta0 = 0.15,
n1 = 20, n2 = 20, y1 = 12, y2 = 8,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = NULL, ne2 = NULL, ye1 = NULL, ye2 = NULL, ae1 = NULL, ae2 = NULL
)
cat("Controlled design posterior probability:", round(result_controlled, 4))
#> Controlled design posterior probability: 0.3871Uncontrolled Design
Single-arm study with historical control.
result_uncontrolled <- pPPsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior',
design = 'uncontrolled',
theta0 = 0.15,
n1 = 20, n2 = 20, y1 = 12, y2 = 4, # y2 represents historical control response
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = NULL, ne2 = NULL, ye1 = NULL, ye2 = NULL, ae1 = NULL, ae2 = NULL
)
cat("Uncontrolled design posterior probability:", round(result_uncontrolled, 4))
#> Uncontrolled design posterior probability: 0.0515External Control Design
Incorporating historical data through power priors.
# External control with 50% borrowing
result_external <- pPPsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior',
design = 'external',
theta0 = 0.15,
n1 = 20, n2 = 20, y1 = 12, y2 = 8,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = 15, ne2 = 25, ye1 = 9, ye2 = 10, ae1 = 0.5, ae2 = 0.5
)
cat("External control posterior probability:", round(result_external, 4))
#> External control posterior probability: 0.3579Sensitivity to Power Prior Parameter
# Evaluate sensitivity to borrowing parameter (varying both ae1 and ae2)
alpha_values <- seq(0, 1, by = 0.2)
borrowing_results <- data.frame(
alpha = alpha_values,
probability = sapply(alpha_values, function(a) {
pPPsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior', design = 'external', theta0 = 0.15,
n1 = 20, n2 = 20, y1 = 12, y2 = 8,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = 15, ne2 = 25, ye1 = 9, ye2 = 10, ae1 = a, ae2 = a
)
})
)
print(borrowing_results)
#> alpha probability
#> 1 0.0 0.3870664
#> 2 0.2 0.3743445
#> 3 0.4 0.3630836
#> 4 0.6 0.3528975
#> 5 0.8 0.3435474
#> 6 1.0 0.3348736
ggplot(borrowing_results, aes(x = alpha, y = probability)) +
geom_line(linewidth = 1.2, color = '#2E8B57') +
geom_point(size = 3, color = '#2E8B57') +
labs(
title = "Sensitivity to Historical Data Borrowing",
x = "Power Prior Parameter (α)",
y = "Posterior Probability",
subtitle = "α = 0: no borrowing, α = 1: full borrowing"
) +
scale_y_continuous(limits = c(0, 1), labels = scales::percent) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(face = "bold"))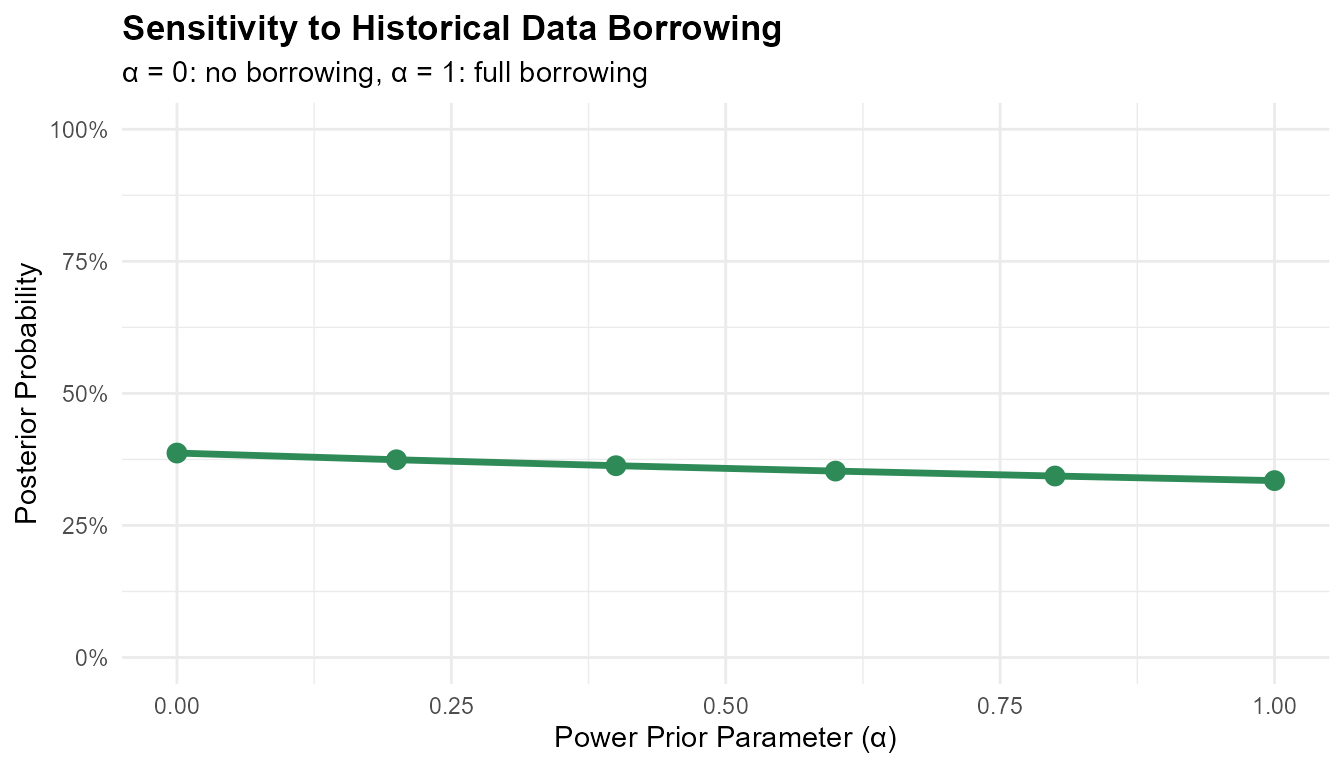
Sample Size Considerations
Power Analysis
# Evaluate power across different sample sizes
sample_sizes <- seq(10, 50, by = 10)
power_results <- data.frame(
n = sample_sizes,
go_prob = sapply(sample_sizes, function(n) {
result <- pGNGsinglebinary(
prob = 'posterior', design = 'controlled',
theta.TV = 0.2, theta.MAV = 0.05, theta.NULL = NULL,
gamma1 = 0.8, gamma2 = 0.2,
pi1 = 0.5, pi2 = 0.3, # Assume true effect of 0.2
n1 = n, n2 = n,
a1 = 0.5, a2 = 0.5, b1 = 0.5, b2 = 0.5,
z = NULL, m1 = NULL, m2 = NULL,
ne1 = NULL, ne2 = NULL, ye1 = NULL, ye2 = NULL, ae1 = NULL, ae2 = NULL
)
result$Go[1]
})
)
print(power_results)
#> n go_prob
#> 1 10 0.2447746
#> 2 20 0.2058666
#> 3 30 0.1762386
#> 4 40 0.2079638
#> 5 50 0.1775540
ggplot(power_results, aes(x = n, y = go_prob)) +
geom_line(linewidth = 1.2, color = '#2E8B57') +
geom_point(size = 3, color = '#2E8B57') +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0.8, linetype = "dashed", color = "red") +
annotate("text", x = 45, y = 0.85, label = "Target: 80%", color = "red") +
labs(
title = "Power Analysis: Sample Size vs Go Probability",
x = "Sample Size (per arm)",
y = "Go Probability",
subtitle = "True treatment effect = 20%"
) +
scale_y_continuous(limits = c(0, 1), labels = scales::percent) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(face = "bold"))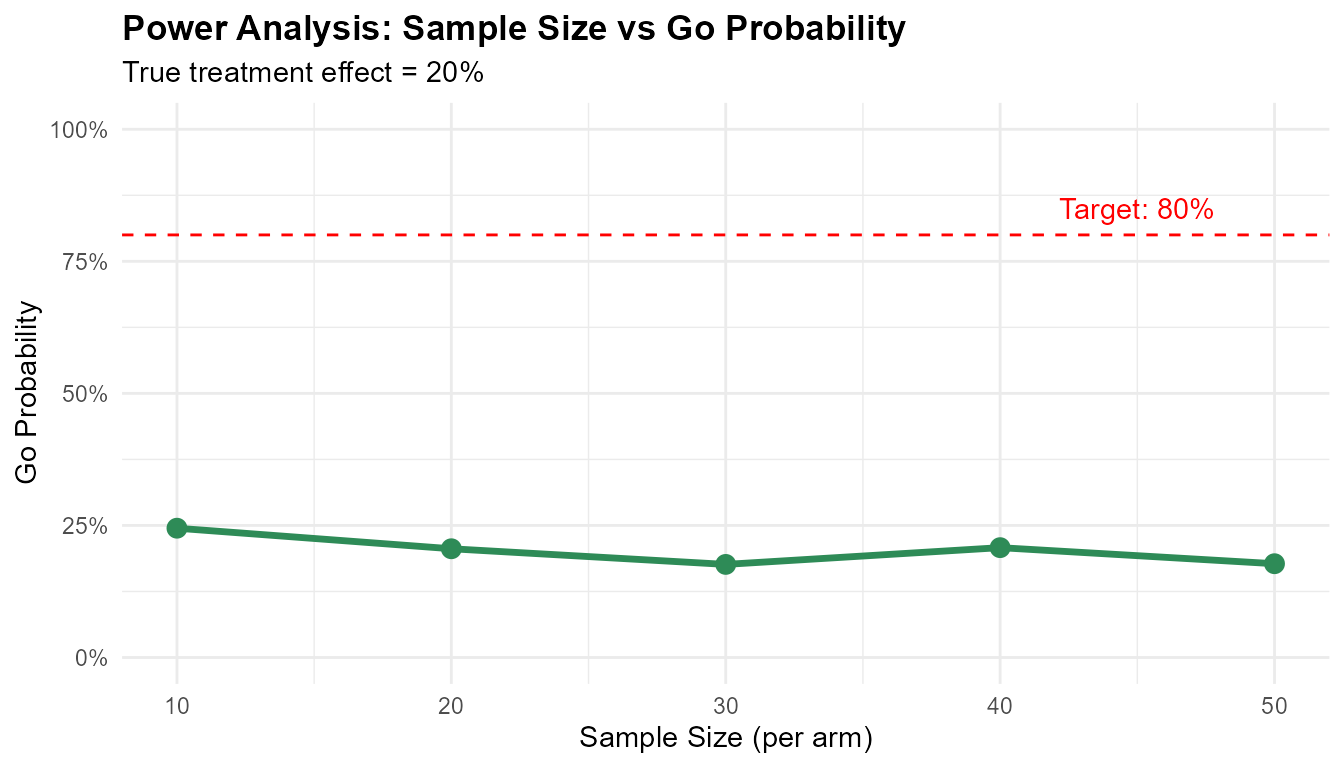
Practical Guidelines
Threshold Selection
When designing a trial, consider:
- θ_TV (Target Value): Set based on clinically meaningful difference
- θ_MAV (Minimum Acceptable Value): Set based on smallest worthwhile effect
- γ₁ (Go threshold): Typically 0.8-0.9 for high confidence
- γ₂ (NoGo threshold): Typically 0.2-0.3 for early stopping
Summary
This vignette demonstrated:
- Basic probability calculations for binary endpoints
- Go/NoGo/Gray decision framework with customizable thresholds
- Operating characteristics evaluation across scenarios
- External control design with power priors
- Sample size considerations for trial planning
The BayesianQDM package provides flexible tools for evidence-based decision making in clinical trials with binary endpoints.